
The respiratory zone is comprised of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar duct, alveolar sac, and alveoli.

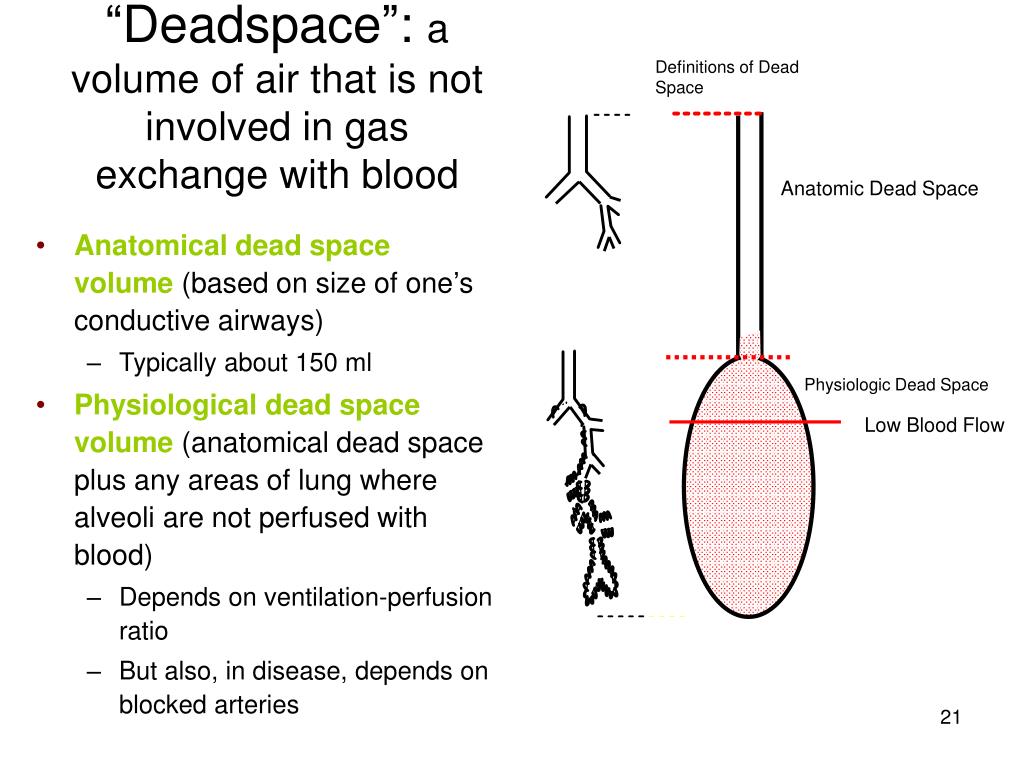
The ratio of physiologic dead space to tidal volume is usually about 1/3. Physiologic or total dead space is equal to anatomic plus alveolar dead space which is the volume of air in the respiratory zone that does not take part in gas exchange. The anatomical dead space plus the volume of any alveoli in which gas exchange is less than normal. It filters, warns, and humidifies air and consists of nose, pharynx, larynx, bronchi, bronchioles, trachea, and terminal bronchioles.

Alveolar dead space is the volume of gas within unperfused alveoli (and thus not participating in gas exchange either) it is usually negligible in the healthy, awake patient. Provides a conduit for inspired air but has no role in gas exchange. Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone (as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zones) and includes the trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles it is approximately 2 mL/kg in the upright position. Physiologic or total dead space is the sum of anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space. Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
